Came across this while searching pain. It is so deadly, I had to write it up.
Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome (CAPS) is a rarely occurring condition leading to death in up to to 1/3 of cases. It can be confused with several other conditions like hemolysis elevated liver enzymes low platelets syndrome (HELLP), thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura(TTP), and hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS); so easily missed. It can present with generalized malaise, abdominal pain, chest pain, shortness of breath and hypertension, altered mental status and seizures. Immediate triple treatment with heparin, IV methylprednisone, and IV immunoglobulins or plasmaphoresis can save lives.
J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016 Mar 29:1-6. [Epub ahead of print]
Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome in pregnancy, a diagnosis that should not be missed.
Hoayek JG(1), Moussa HN(1), Rehman HA(1), Nasab SH(1), Blackwell SC(1), Sibai BM(1).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27023104
Over half give a history of
- previous abortions or fetal losses
- previous DVT or arterial thrombosis;
- a third have associated systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and the rest have lupus-like disease or other autoimmune diseases
However, that means nearly 1/2 give NO history
- mortality has decreased from 100% before 1980 to 33% now.
- Though occurrence in pregnancy is very bad, the highest risk period is post partum
Presentation patterns:
- kidney involvement (53%) – renal insufficiency, hypertension, and proteinuria,
- pulmonary involvement (48%)- acute respiratory syndrome, pulmonary emboli, and pulmonary hemorrhage.
- cerebral involvement (58%), – encephalopathy, strokes and seizures,
- cardiac involvement (55%) in the form of heart failure, myocardial infarctions, and valve defects
- Liver involvement with abnormal liver function tests
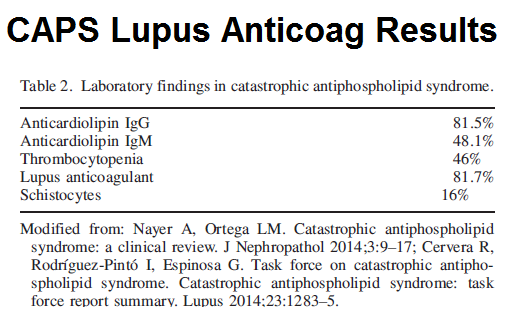
- Hematologic – bone marrow necrosis and thrombocytopenia (low platelets); in <25% – Thrombotic microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA) with Schistocytes (seen in 16%) in blood
Diagnostic criteria:
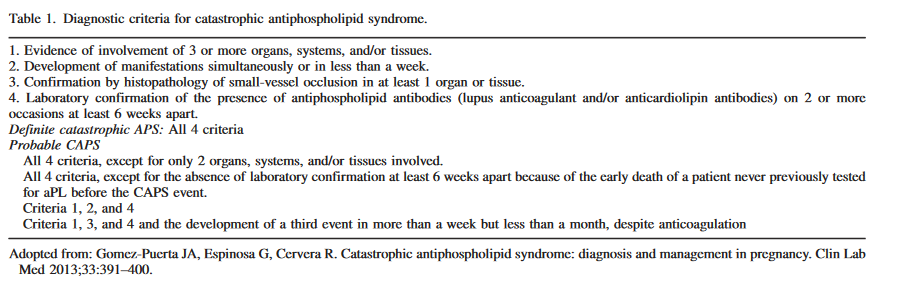 Presence of Lupus like anticoagulant antibodies is often seen: – they generally like two values 6 weeks apart but this is no use in a critical situation.
Presence of Lupus like anticoagulant antibodies is often seen: – they generally like two values 6 weeks apart but this is no use in a critical situation.
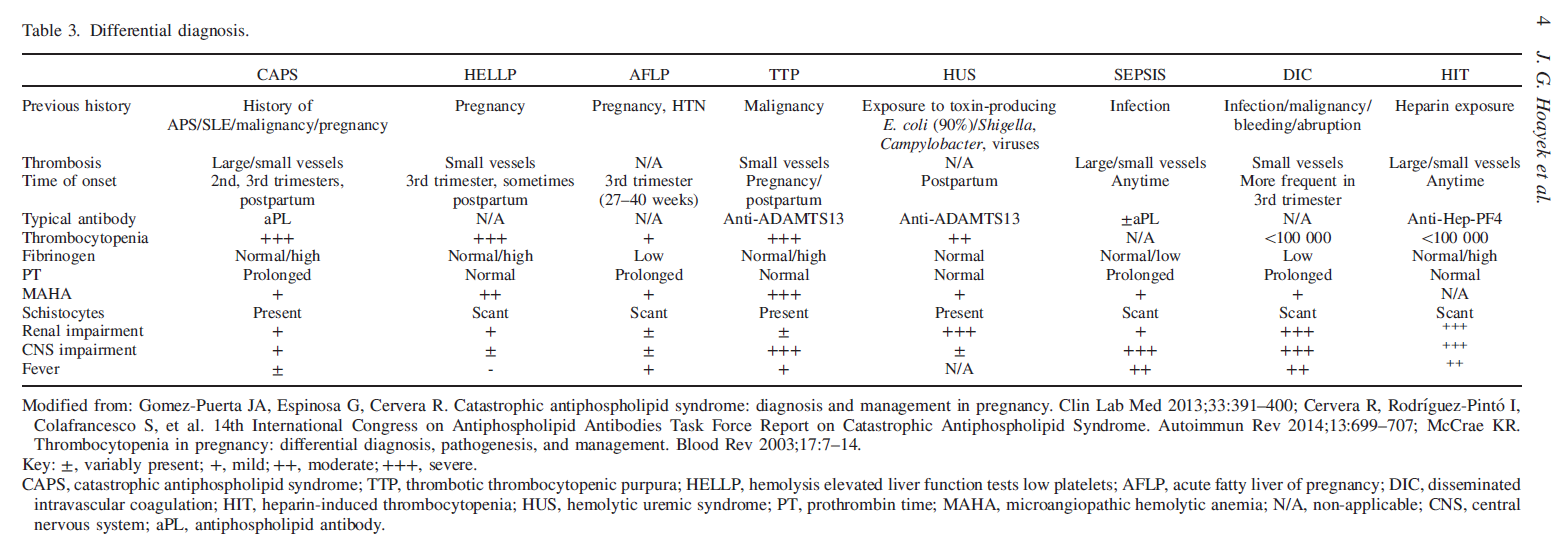
Main differentiations are two mainly liver diseases:
Acute fatty liver Disease of Pregnancy AFLP
- Nelson, David B., Nicole P. Yost, and F. Gary Cunningham. “Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: clinical outcomes and expected duration of recovery.” American journal of obstetrics and gynecology 209.5 (2013): 456-e1.
- More than 90% of these women had at least 1 of these findings or combinations thereof with liver failure:
1- to 2-week history of malaise, anorexia, N/V, mid-epigastric or RUQ pain,headache, jaundice, and who is ill-appearing on physical exam-persistent nausea and vomiting (57%)
-hypertension (57%)
– abdominal pain (53%). - ill looking and jaundice, a feature
- A combination of hepatic and renal dysfunction was nearly universal, but with variable severity.
- “hypoglycemia, hypertension, proteinuria, ascites, bleeding from severe coagulopathy, and hepatic encephalopathy may also be present.”
- “Procoagulant synthesis was impaired in more than three-fourths of the women, which served to intensify obstetric hemorrhage for which 50% of the 51 women received blood and component transfusion”
- “Laboratory findings reveal elevated white blood count, and a normal to slightly reduced platelet count. Coagulation studies show low Fibrinogen, prolonged pro-
thrombin time (PT), low levels of antithrombin, high levels of liver enzymes, creatinine, uric acid, and bilirubin.”
HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count) syndrome
- shortness of breath
- generalized malaise,
- epigastric or right upper quadrant(RUQ) pain,
- nausea/vomiting (N/V)
- nonspecific flu-like symptoms
- Severe hypertension (systolic >160 mmHg, diastolic >110
- preeclampsia common
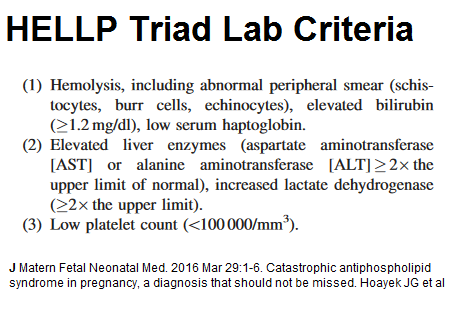
Lab Criteria includes:
Treatment approach includes:
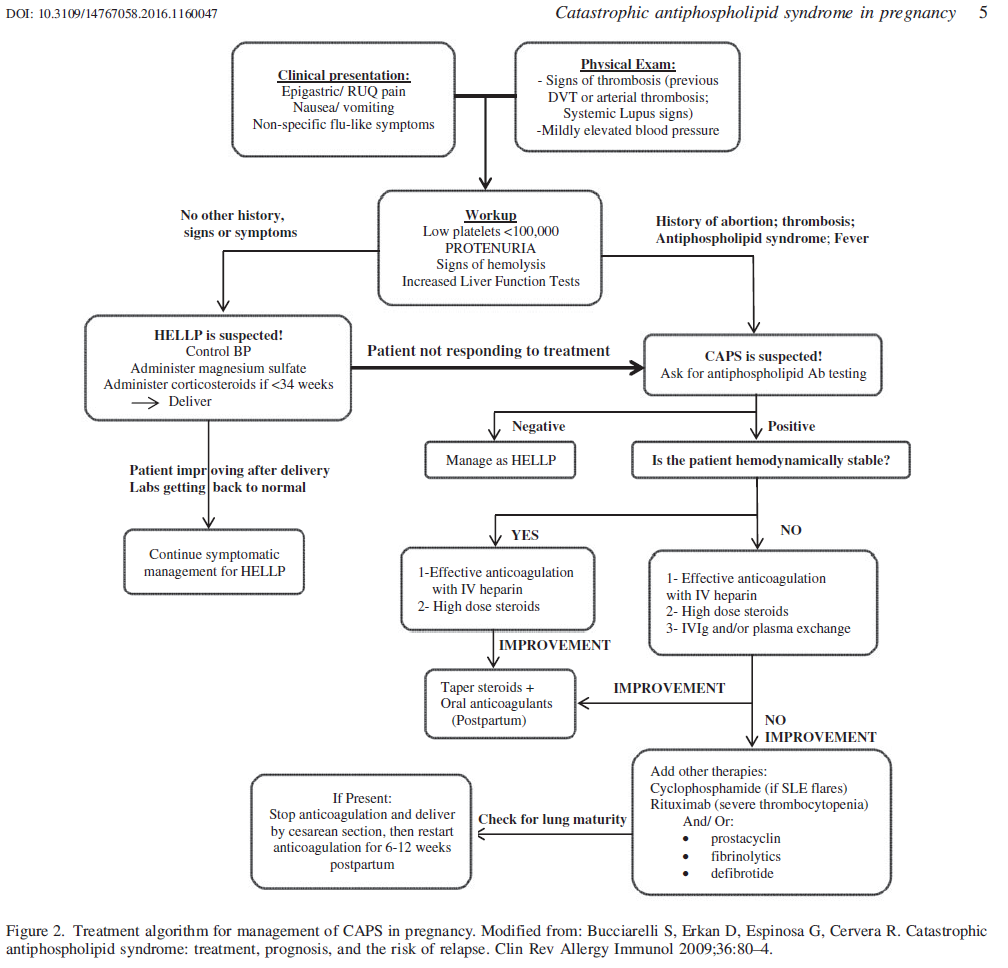 Anticoagulation is with 0.5mg/kg/day – 1 mg/kg BID subcut
Anticoagulation is with 0.5mg/kg/day – 1 mg/kg BID subcut
IV steroids is methylprednisolone 1gm/day IV for 3-5 days (hard on veins)
IVIG (gamma globulins) is 0.4 g/day/kg body weight for 4–5 d.
Plasma exchange – “most often used procedure is removal of 2–3 liters of plasma for a minimum of 3–5 d.”
Bleeding can be reversed with fresh frozen plasma.
Lung involvement with CT imaging ground glass appearance is very bad.
Comment – Bottom line is to recognize early, treat early, and use triad treatment – heparin, methylprednisolone and gamma globulin or plasma exchange.
Sorry to authors for using their tables – if they find offensive I will remove – but I found it compelling topic so presented.