A “single i.v. bolus of ketamine (0.2 mg/kg) over 1–2 min will rapidly dissolve suicidal ideation” and its effect will last aat least 10 days. I find this an exciting innovation that could prevent a big unnecessary killer. This is just an extension of the finding that chronic resistant depression can remit withing 15 minutes of 0.5 mg/kg ketamine run in over 40 minutes and its effects last 3-7 days.
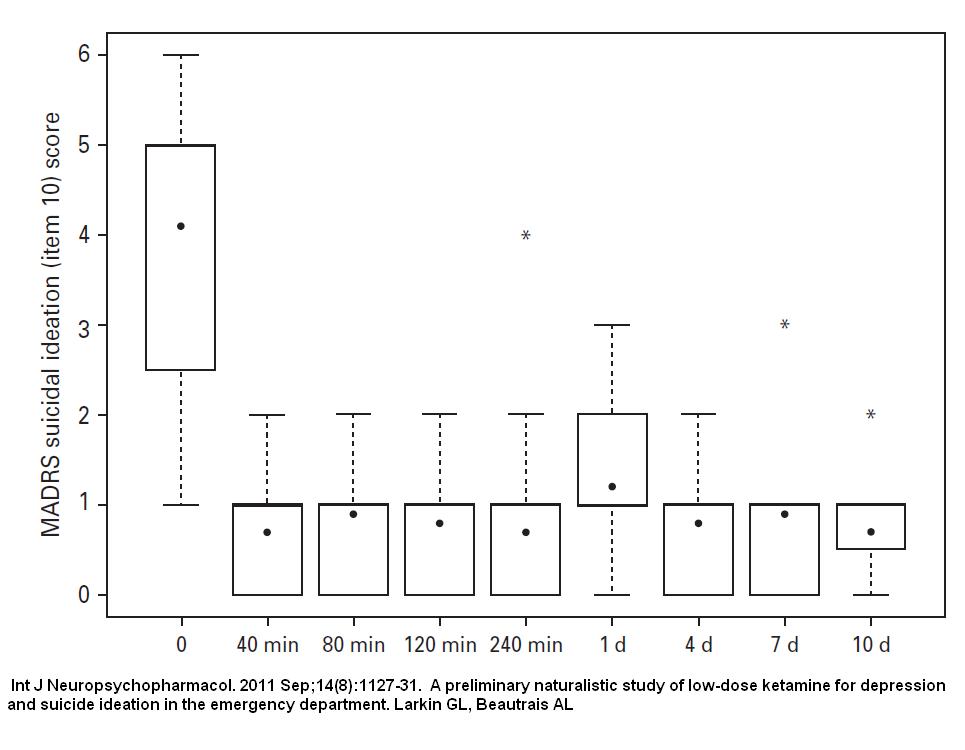
Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011 Sep;14(8):1127-31.
A preliminary naturalistic study of low-dose ketamine for depression and suicide ideation in the emergency department.
Larkin GL, Beautrais AL abstract here
retracted but:
Wilkinson ST, Ballard ED, Bloch MH, Mathew SJ, Murrough JW, Feder A, Sos P, Wang G, Zarate CA Jr, Sanacora G. The Effect of a Single Dose of Intravenous Ketamine on Suicidal Ideation: A Systematic Review and Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis. Am J Psychiatry. 2018 Feb 1;175(2):150-158
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28969441/
1 week benefit
- 14 cases in emergency room
- Given 0.2 mg/kg over 1-2 minutes ketamine – this would be 12-25 mg ketamine range
- “>Suicidality rapidly fell and lasted at least 10 days:
Thsi relief of suicidality was found to occur in cancer subjects in a separate article:
J Palliat Med. 2011 Apr;14(4):389.
Ketamine alleviates fear, depression, and suicidal ideation in terminally ill patients.
Thangathurai D, Mogos M. no abstract
Comment –
I wrote about Ketamine and depression in a separate article:
Depression is a Form of Pain and Ketamine May be a Cure if One Can Make It Last
I presented these findings to a very reluctantly received (by key speaker) meeting of physicians. I suppose anything new is considered suspect. I hope since it was now reviewed as a new innovation by NATURE journal, it will receive more respect:
Nature. 2011 Jun 15;475(7354):91-5. doi: 10.1038/nature10130.
NMDA receptor blockade at rest triggers rapid behavioural antidepressant responses.
Autry AE, Adachi M, Nosyreva E, Na ES, Los MF, Cheng PF, Kavalali ET, Monteggia LM.Department of Psychiatry, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, 5323
Harry Hines Boulevard, Dallas, Texas 75390-9111, USA. abstract from here
Clinical studies consistently demonstrate that a single sub-psychomimetic dose of ketamine, an ionotropic glutamatergic NMDAR (N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor) antagonist, produces fast-acting antidepressant responses in patients suffering from major depressive disorder, although the underlying mechanism is unclear. Depressed patients report the alleviation of major depressive disorder symptoms within two hours of a single, low-dose intravenous infusion of ketamine, with effects lasting up to two weeks, unlike traditional antidepressants (serotonin re-uptake inhibitors), which take weeks to reach efficacy. This delay is a major drawback to current therapies for major depressive disorder and faster-acting antidepressants are needed, particularly for suicide-risk patients. The ability of ketamine to produce rapidly acting, long-lasting antidepressant responses in depressed patients provides a unique opportunity to investigate underlying
cellular mechanisms. Here we show that ketamine and other NMDAR antagonists produce fast-acting behavioural antidepressant-like effects in mouse models, and that these effects depend on the rapid synthesis of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. We find that the ketamine-mediated blockade of NMDAR at rest deactivates eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2) kinase (also called CaMKIII), resulting in reduced eEF2 phosphorylation and de-suppression of translation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Furthermore, we find that inhibitors of eEF2 kinase induce
fast-acting behavioural antidepressant-like effects. Our findings indicate that the regulation of protein synthesis by spontaneous neurotransmission may serve as a viable therapeutic target for the development of fast-acting antidepressants.
I prefer Deltoid IM injections of 10 mg every 15 minutes up to 30 mg total if no depersonalization reaction.
Addendum:
This was confirmed in a 2017 controlled trial:
Grunebaum, Michael F., et al.
Ketamine for Rapid Reduction of Suicidal Thoughts in Major Depression: A Midazolam-Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial.
American Journal of Psychiatry (2017) in press
https://ajp.psychiatryonline.org/doi/abs/10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.17060647?journalCode=ajp
More recently, Ketamine was found very useful in subjects that had attempted:
J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2018 Apr;38(2):149-150.
doi:10.1097/JCP.0000000000000852.
Intravenous Ketamine Relieves Pain and Depression After Traumatic Suicide
Attempts: A Case Series.
Mischel N et al
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29424806
no abstract
I have had suicidal patient that I have given ketamine to, as well as urgent referral to psychiatrists. Some psychiatrist had look with a jaded eye on that practice but it has now been validated.

Pingback: Ketamine For Depression Confirmed | Pain Medical Musing
Pingback: 14 Days Ketamine Induced Presistent Depression Relief in Adolescent Rats | Pain Medical Musing