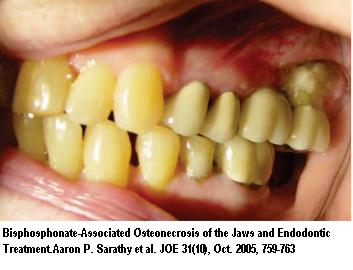
Osteonecrosis mandible from mostly IV biphosphamates can be a real hazard in cancer treatments – now it looks like teriparatide – human recombinant pararthyroid hormone peptide 1-34 – was able to help recovery
Head Neck. 2010 Mar 22. [Epub ahead of print]
Successful treatment of advanced bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the mandible with adjunctive teriparatide therapy.
Lee JJ, Cheng SJ, Jeng JH, Chiang CP, Lau HP, Kok SH. abstract
- “78-year-old osteoporotic woman with osteonecrosis of the mandible related to alendronate therapy”
- “daily subcutaneous injection of 20 microg teriparatide, as usually recommended for treatment of osteoporosis”
- “RESULTS.: The oral mucosa completely regrew, and pain subsided 4 weeks after the initiation of teriparatide administration. Progressive bone regeneration was found during and after the 6-month period of teriparatide therapy”
Comment – looks great but debridement is necessary to area. Won’t be cheap.
addendum:
There is evidence that drugs like pamidronate allow bacteria to stick to bone better and cause an osteomyelitis:
Pamidronate Enhances Bacterial Adhesion to Bone Hydroxyapatite. Another Puzzle in the Pathology of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw?
Marcin Kos et al
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 71:1010-1016, 2013
Long term antibiotics can produce healing combined with local treatments: – only B groups results are shown as they got 100% recovery
Hoefert S, Eufinger H: Relevance of a prolonged preoperative antibiotic
regime in the treatment of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis
of the jaw. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69:362, 2011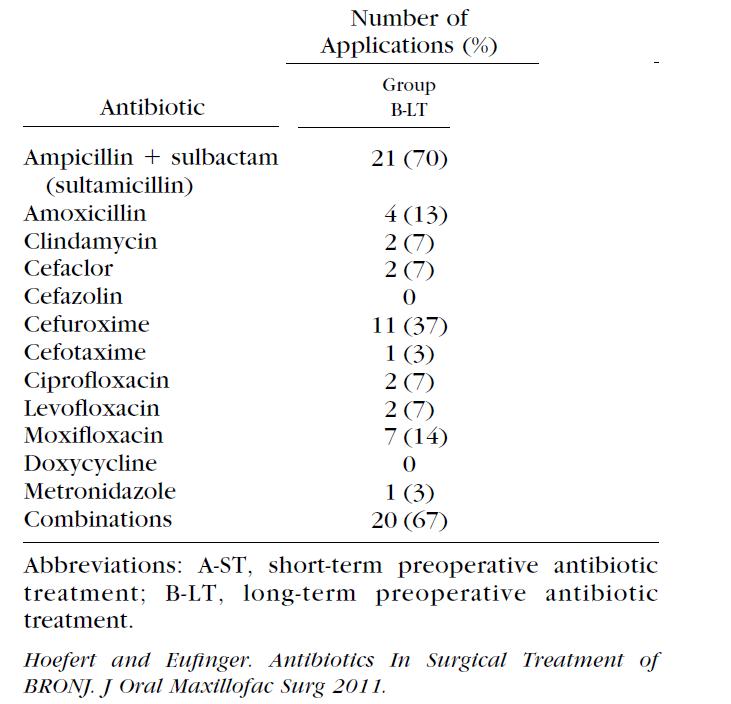
- “surgical procedure consisted of sequestrectomy, block resection , bone surface smoothing, surgical cleaning of periodontal pockets and root surface
smoothing of the adjacent teeth, extraction of teeth that needed removal, and a tension-free soft tissue coverage” - “Preoperatively antibiotics were given intravenously for a median of 1 to 3 days and after operation for a median of 7 days
(Table 3). After discharge from hospital, oral antibiotic therapy followed. “ - “Sutures were removed after the 14th day if necessary. Sutures that could not be removed easily were left for self-resorption.”
- “In addition, chlorhexidine mouth rinses 0.12% (CHX) once a day were recommended.”
- “median duration of preoperative antibiotic therapy was 31 days (23 to 54 days) orally and 1 day intravenously (1 to 3 days). Postoperatively,
the patients received antibiotics intravenously for 7 days (3 to 14 days) and afterward orally for another 12 days (5 to 47 days;” - “Further antibiotic therapy was adjusted to the antibiogram-resistogram profile if necessary. Fluconazole (Diflucan 50; Pfizer, Berlin, Germany)
was added for 3 to 4 weeks if microbiologic findings showed Candida” - Comment – there is strong usage of sultamicillin (a peniciliin plus a beta-lactamase inhibitor)- a Phizer product Unasyn that ?could be gotten by emergency release though I did find an out of country site for purchase:
http://www.rxheads.com/unasyn-oral-p236
