It has always been vague on the fine points of this techique. A beautiful account for this procedure is available in this newsletter:
http://www.asra.com/content/documents/nov-13_asra_news.pdf
on pages 14-17
I have included a summary for those who can’t reach it.
Ultrasound-guided Interventions for Calcific Tendinosis of the Rotator Cuff.
Peter H. Cheng, Philip Peng.
American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine Newsletter Nov 2013;14-17
http://www.asra.com/content/documents/nov-13_asra_news.pdf
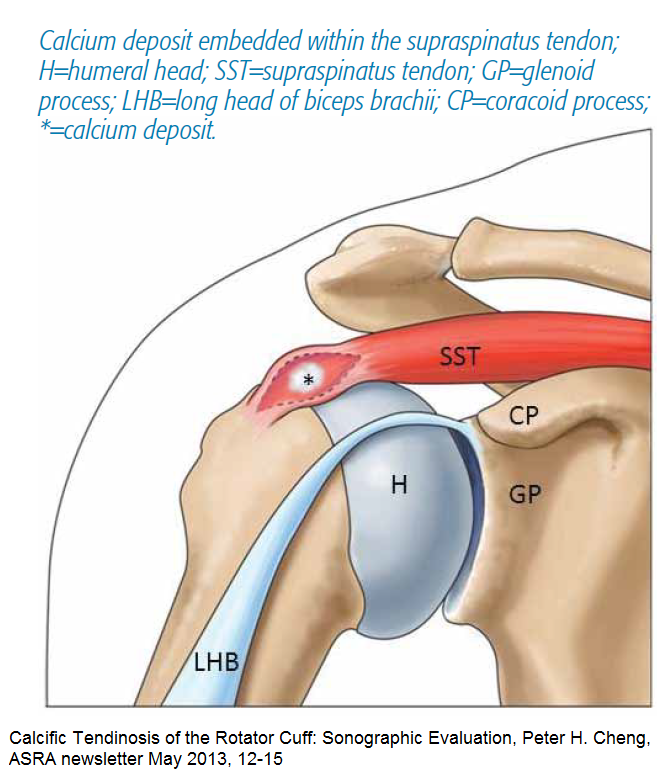
In supraspinatus, close to insertion
- skin and tissue local with 25 gauge needle local
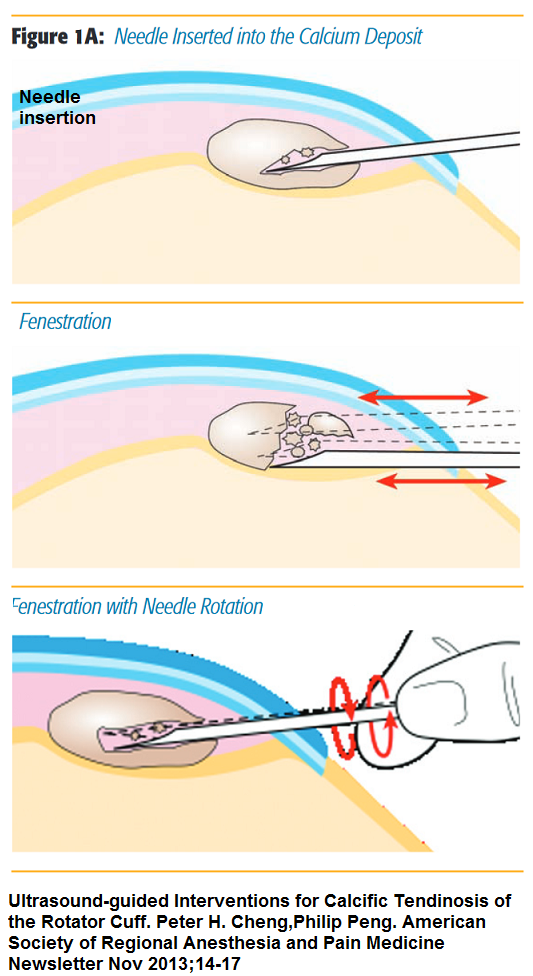
- 16 or 18 gauge Tuohy needle (epidural less pointy needle) into the calcium deposit.
- might meet stiff resistance as the needle fractures the dense calcium.
- Multiple “passes” – less resistance; hitting it from difference angles helps
- Rotating the needle helps
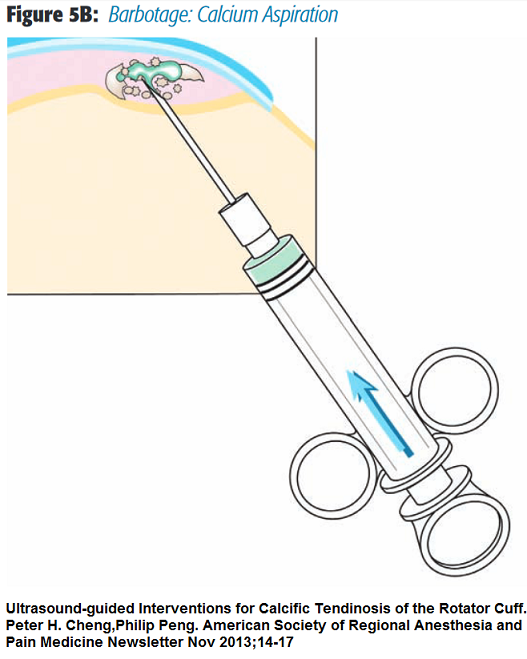
- Barbotage = Repeatedly inject and aspirate saline though if gets plugged will have to remove and re-insert
Can be done with 2 needles which saves time. Hint- have bevels face each other so fluid in one and out other
- Afterwards, inject subacromial bursa with triamcinlonone
Use of steroid found efficacious:
Acta Radiol. 2017 Aug;58(8):964-970. doi: 10.1177/0284185116678275.
Efficacy of triamcinolone acetate and methylprednisolone acetonide for intrabursal injection after ultrasound-guided percutaneous treatment in painful shoulder calcific tendonitis: a randomized controlled trial.
Battaglia M et al
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27856801
- sling
Article did this under ultrasound control.
They did refer to one article that said it was not necessary to remove calcifications but 2 authors found elsewise.