Recently, nortriptyline has been touted as good anti-neuropathic drug but thoughts of its use have extended into use for chronic pain in general. Well, it doesn’t work for back pain, sciatica or migraines so that might need reanalysis.
A recent Cochrane review concludes:
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 8;1:CD011209. [Epub ahead of print]
Nortriptyline for neuropathic pain in adults.
Derry S. et al
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25569864
“We found little evidence to support the use of nortriptyline to treat the neuropathic pain conditions included in this review. There were no studies in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. The studies were methodologically flawed, largely due to small size, and potentially subject to major bias. The results of this review do not support the use of nortriptyline as a first line treatment. Effective medicines with much greater supportive evidence are available, such as duloxetine and pregabalin.”
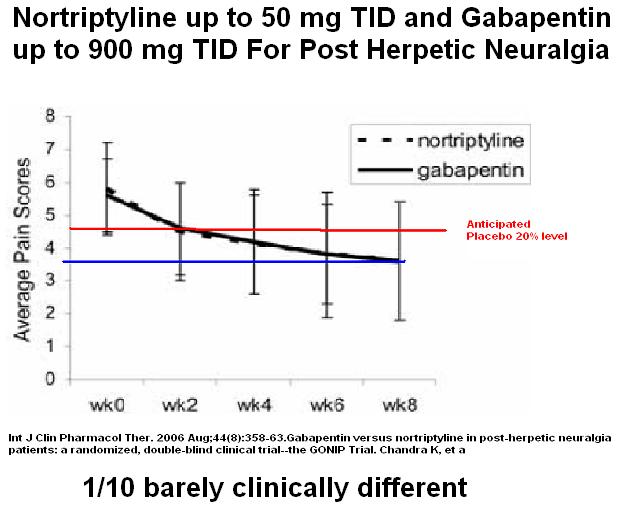
A study from India found nortriptyline reduced post-herpetic neuralgia pains by 42%: Often placebo is considered to give a 20% reduction so that leaves a 22% reduction.
Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Aug;44(8):358-63.
Gabapentin versus nortriptyline in post-herpetic neuralgia patients: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial–the GONIP Trial.
Chandra K, Shafiq N, Pandhi P, Gupta S, Malhotra S.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16961166
When plotted out it represented a drop of 1/10 on VAS scale from anticipated placebo – the minimum accepted by FDA for significant reduction – but is not really clinically significant (drop 2 usually expected)
Fortunately, combining it with Gabapentin seemed to augment its effect.
Another study in post herpetic neuralgia;
Nortriptyline versus amitriptyline in postherpetic neuralgia A randomized trial.
C. Peter N. Watson, Lee Vernich, Mary Chipman, and Ken Reed.
Neurology October 1998 vol. 51 no. 4 1166-1171
http://www.neurology.org/content/51/4/1166.short
- 17 responders and 13 non-responders
- Did not publish actual data so cannot comment on.
- Was a cross over from an opioid trial 1 month prior and that could change everything.
—————————
A Canadian study on Neuropathic pain found nortriptyline reduced pains from 5.4 to 3.2 but again there is a lack of a placebo group. If one anticipated a 20% drop with placebo then placebo would make it down to 4.3 – making the diference 1.1/10 – still barely significant
Gilron, Ian, Joan M. Bailey, Dongsheng Tu, Ronald R. Holden, Alan C. Jackson, and Robyn L. Houlden.
Nortriptyline and gabapentin, alone and in combination for neuropathic pain: a double-blind, randomised controlled crossover trial.
The Lancet 374, no. 9697 (2009): 1252-1261.
http://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(09)61081-3/abstract?version=printerFriendly
——————————
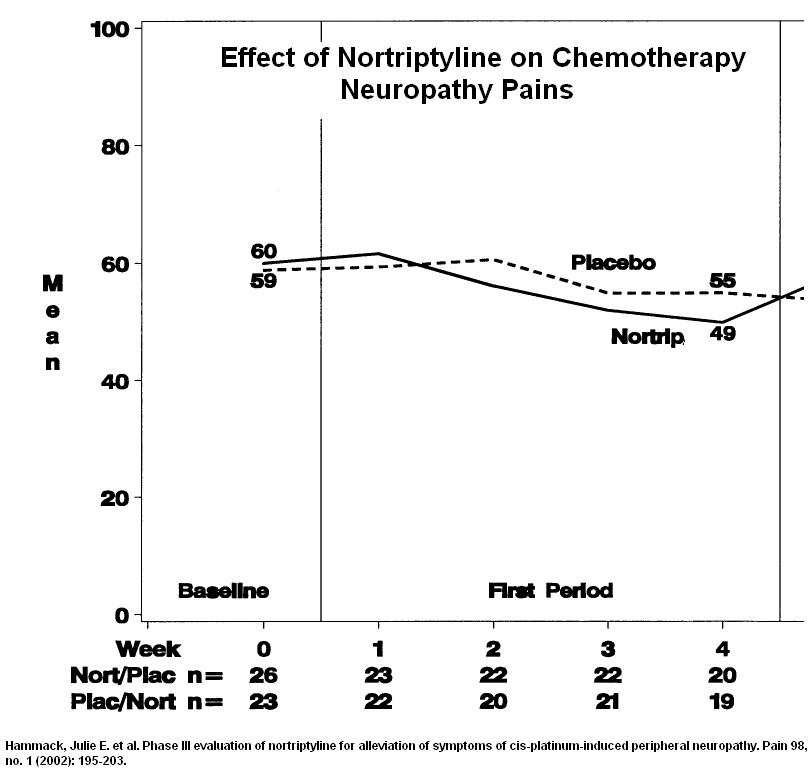
Prior to cross-over, chemotherapy induced neuropathy pains did not seem to benefit from nortriptyline – after cross over, there was a modest effect but I suspect cross-over effects (after cross over, other measures could have been implemented that could have made a difference).
Hammack, Julie E., John C. Michalak, Charles L. Loprinzi, Jeff A. Sloan, Paul J. Novotny, Gamini S. Soori, Maria Tria Tirona, Kendrith M. Rowland Jr, Philip J. Stella, and Joanne A. Johnson.
Phase III evaluation of nortriptyline for alleviation of symptoms of cis-platinum-induced peripheral neuropathy.
Pain 98, no. 1 (2002): 195-203.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12098632
—————————————————
Ashamed to mention that nortriptyline at a pathetically low dose of 10 mg/day was not effective and B12 shots faired better for Diabetic neuropathy:
Talaei, Afsaneh, Mansour Siavash, Hamid Majidi, and Ali Chehrei.
Vitamin B12 may be more effective than nortriptyline in improving painful diabetic neuropathy.
International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition 60, no. s5 (2009): 71-76.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19212856
A consensus reported there was insufficient evidence that nortriptyline was effective in diabetic neuropathy:
Neurology. 2011 May 17;76(20):1758-65.
Evidence-based guideline: Treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and
Rehabilitation.
Bril V, England J, Franklin GM, Backonja M, Cohen J, Del Toro D, Feldman E, Iverson DJ, Perkins B, Russell JW, Zochodne D;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3100130/pdf/znl1758.pdf
————————–
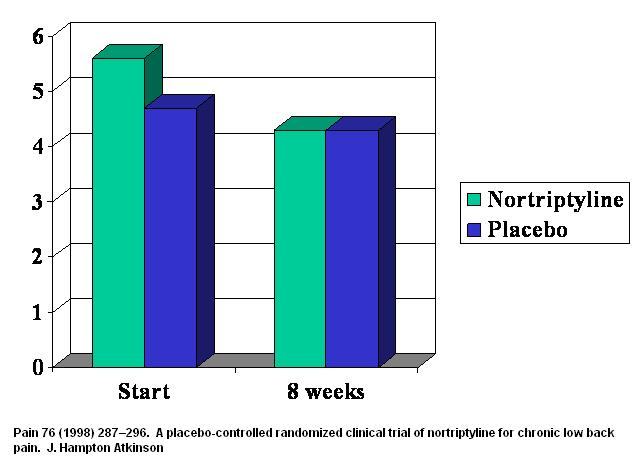
In Chronic back pain, there was not much difference:
Atkinson, J. Hampton, Mark A. Slater, Rebecca A. Williams, Sidney Zisook, Thomas L. Patterson, Igor Grant, Dennis R. Wahlgren, Ian Abramson, and Steven R. Garfin.
A placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial of nortriptyline for chronic low back pain.
Pain 76, no. 3 (1998): 287-296.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9718247
———————————-
In radiculopathy, it did not make much difference:
Khoromi, Suzan, Lihong Cui, Lisa Nackers, and Mitchell B. Max.
Morphine, nortriptyline and their combination vs. placebo in patients with chronic lumbar root pain.
Pain 130, no. 1 (2007): 66-75.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1974876/pdf/nihms26039.pdf
- Only 28 out of 61 patients completed study
- “none of the treatments produced significant reductions in average leg pain or other leg or back pain scores.” Pain reduction, relative to placebo treatment was 14% for nortriptyline (95% CI= [−2%, 30%]), 7% for morphine (95% CI= [−8%, 22%]), and 7% for the combination treatment (95% CI= [−4%, 18%]). “
- “Mean doses were: nortriptyline alone, 84 +/− 24.44 (SD)mg/day; morphine alone, 62 +/−29mg/day; and combination, morphine, 49 +/−27 mg/day plus nortriptyline, 55 mg+/− 33.18 mg/day”
——————————-
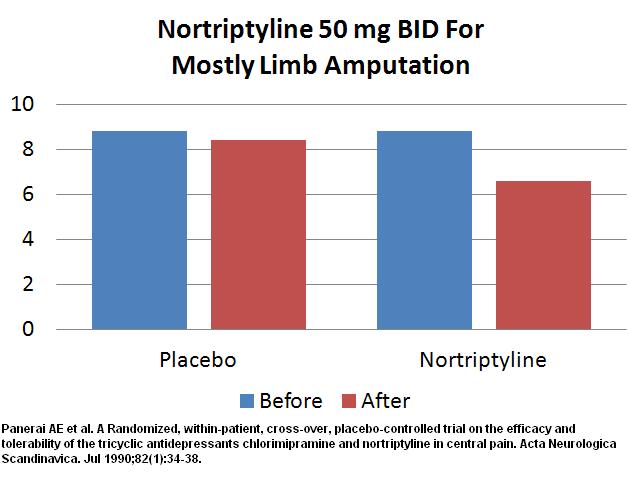
In post amputation pains, there is modest benefit at 50 mg bid: (drop of 1.8/10 over placebo)
—————————
Nortriptyline did not work in Fibromyalgia:
A double-blind, randomized, controlled study of amitriptyline,nortriptyline and placebo in patients with fibromyalgia.An analysis of outcome measures
R.E. Heymann, M. Helfenstein, D. Feldman
Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2001; 19: 697-702.
http://www.clinexprheumatol.org/article.asp?a=1199
“An improvement of 36.5% in the amitriptyline group, 26.6% in the nortriptyline group, and 24% in the placebo group was noted.”
—————————-
Low dose Nortriptyline (20 mg/day) had no effect on migraines unless propranolol added:
Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2009 Dec;67(4):973-7.
A double-blind randomized controlled trial of low doses of propranolol, nortriptyline, and the combination of propranolol and nortriptyline for the preventive treatment of migraine.
Domingues RB, Silva AL, Domingues SA, Aquino CC, Kuster GW
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20069203
Comment – you can probably tell, I do not think much of antidepressants in chronic pain. It does have modest effects but only in some neuropathic pain conditions… Can’t prove any effectiveness in migraines, back pains or sciatica. Given that only 23.7% of patients came under control with neuropathic pain in one recent study, I am convinced anti-depressants could be tried but combinations are going to be needed.
Could use feedback here..