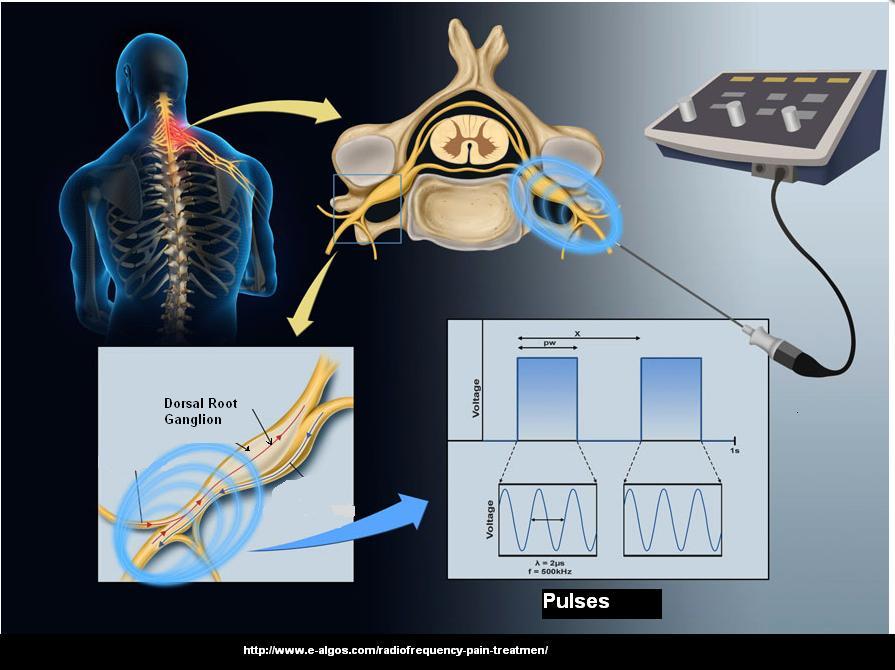
- To round out my discussion of post herpetic neuralgia, I have included an article on pulse radiofreqency to dorsal root ganglion in spine – a benign, not destructive, resetting of senstivity of the ganglion by 41 degree centrigrade heat. My feeling is, intercostal nerve areas are safer to do than ganglion blocks, and semineurolytic agents, perhaps repeated several times – would be alot easier and safer. Details on approach to infraorbital block displayed.
Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008 Sep;52(8):1140-3.
Effect of pulsed radiofrequency for postherpetic neuralgia.
Kim YH, Lee CJ, Lee SC, Huh J, Nahm FS, Kim HZ, Lee MK.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18840116
- 49 refractory post herpetic neuralgia cases
- Criteria – patients need to “responded to a diagnostic block (twice, weekly) with 0.25% ropivacaine 1 ml at the DRG of the lumbar, thoracic and cervical levels with fluoroscopic guidance.”
- Method – “10-cm electrode with a 5mm active tip (22G,Radionics SMK-C10; Radionics Inc. Burlington, MA), was inserted adjacent to the DRG with fluoroscopic guidance and controlled so that the tip was projected behind the upper lateral part of the facet column in an antero-posterior view and positioned in the dorsocranial quadrant of the intervertebral foramen in the
lateral view. The correct needle position was confirmed by electrical 50-Hz stimulation. A tingling sensation in the corresponding dermatome had to be obtained between 0.4 and 0.6V. After obtaining the appropriate stimulation, PRF was applied three times at the corresponding level to 42 1C for 120s. The impedance was maintained below 600 O.When the impedance exceeded 600O, saline was injected.” - Results:

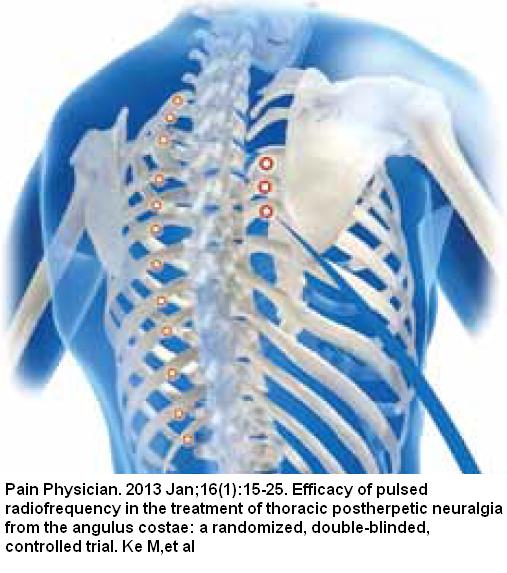
The nerve root ganglion does not have to be the target – The intercostal nerve was used in one study:
Pain Physician. 2013 Jan;16(1):15-25.
Efficacy of pulsed radiofrequency in the treatment of thoracic postherpetic neuralgia from the angulus costae: a randomized, double-blinded, controlled trial.
Ke M, Yinghui F, Yi J, Xeuhua H, Xiaoming L, Zhijun C, Chao H, Yingwei W.
http://www.painphysicianjournal.com/2013/january/2013;16;15-25.pdf
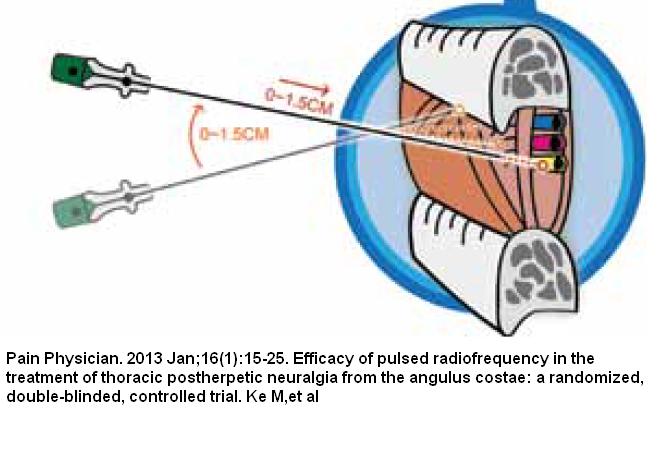
Traditional technique was used to find nerve root – inject onto rib and then insert under: ( near the spine the nerve is more mid point between ribs rather than just under though)
- Positioning – Generally the puncture depth that is considered safe and effective is less than 1.5 cm beneath the rib. The paresthesia thus induced should be over the region
involving the pain, and ideally, the area of paresthesia should cross the midclavicular line, or to the approximate edge of the sternum.
- Technique – (inserted just past where rib joins transverse process) The electrode needle was fixed by the index finger and thumb at the determined puncture point of the skin to maintain the depth and position of the needle tip.The mode of the PRF instrument was turned into the working mode subsequently to initiate treatment. The PRF was done using the Pain Management Generator (PM-230, Baylis Medical Company, Montreal, Canada). The PRF settings were 42°C, 120 seconds/twice for the same level.
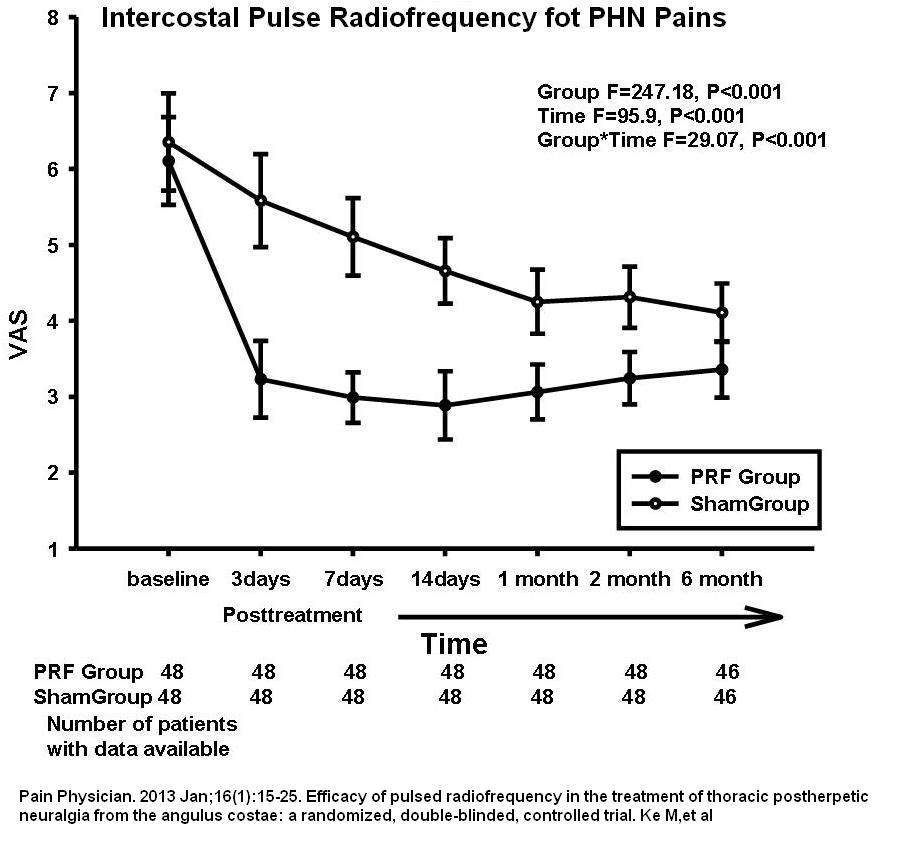
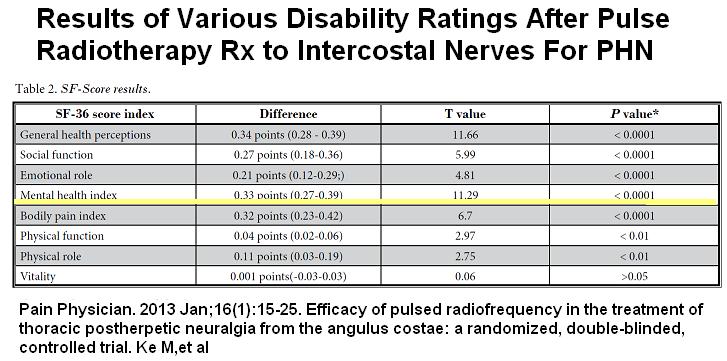
- Results:
Wellbeing was obviously improved following treatment – again confirming mental health is driven by the pain and not visa-versa:
- Side effects – one patient had puncture to intercostal artery which caused a wound which quickly healed.
- They make a compelling case for using intercostal nerve for pulse radiofrequency:
“A study using PRF for the treatment of thoracic postoperative pain suggested that targeting the DRG can provide greater long-term pain relief than targeting the intercostal nerve (18). However, DRG targeting carries with it the potential risk of pneumothorax. In addition, it has been reported that there is a risk of damage to the the artery of Adamkiewicz (ARM) when puncturing through the intervertebral foramen, and paraplegia can be caused by transforaminal injection (39). Besides, it is difficult to maintain the vertical position between the needle tip and the DRG neuron. Therefore, the procedure of PRF puncture from the angulus costae is easier and has a lower potential risk compared to the thoracic puncture methodology targeting the DRG”
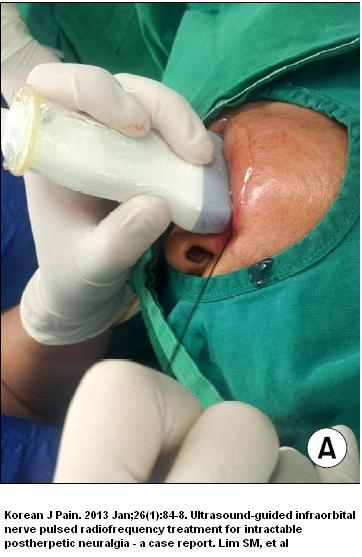
This technique was adapted to be used on the face to the infraorbital nerve:
Korean J Pain. 2013 Jan;26(1):84-8.
Ultrasound-guided infraorbital nerve pulsed radiofrequency treatment for intractable postherpetic neuralgia – a case report.
Lim SM, Park HL, Moon HY, Kang KH, Kang H, Baek CH, Jung YH, Kim JY, Koo GH, Shin
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3546218/pdf/kjpain-26-84.pdf
- Interestingly, the probe was inserted inferiorly to the infraorbital foramen as the infaorbital margin protects the orbit: (it is 1-1.5 cm below rim)
This would look like this in a model:
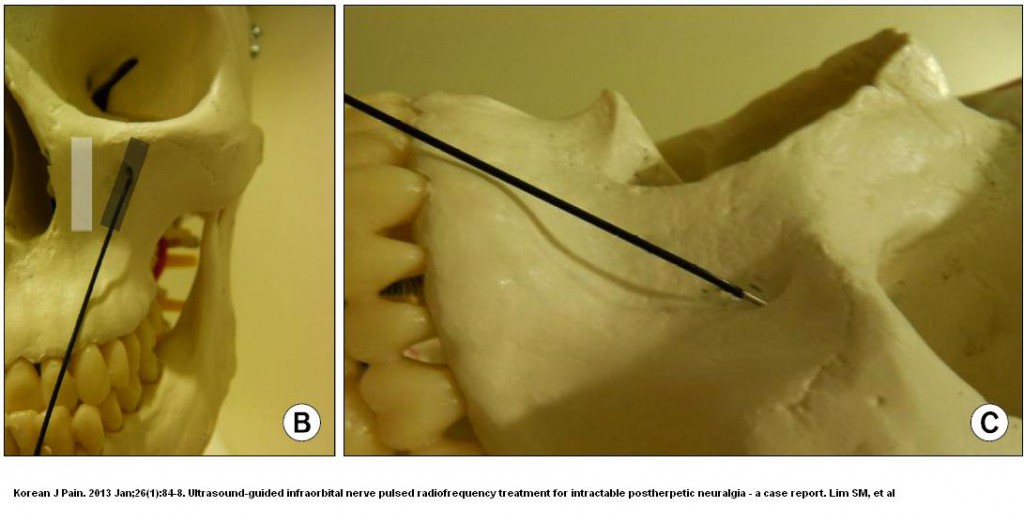
- Did 3 pulses of 42 degrees – each 120 seconds
- His pain went from 9/10 (had for 6 + months) to 1-2/10 even 12 months later
Comment – an effective technique that is not available here. Not sure 4-5% tetracaine (pontociane) or 5-10% lidocaine could not work as well:
J Clin Anesth. 2002 Feb;14(1):39-41.
Intercostal nerve block with 5% tetracaine for chronic pain syndromes.
Doi K, Nikai T, Sakura S, Saito Y.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11880021
- 5% tetracaine with 10 % dextrose used though not sure latter all that important.
- 1 cc injected in most affected rib level for severe chronic rib level pains
- used in post thoracotomy, post esophageal surgery , and post herpetic neurlagia
- remarkable relief lasting 5 days to 9 months. Beauty of it is that it can be readily reinjected – and if one can stick to a 27-30 gauge needle, less likely to puncture lung.
Clin J Pain. 2001 Dec;17(4):323-6.
High-concentration tetracaine for the management of trigeminal neuralgia: quantitative assessment of sensory function after peripheral nerve block.
Radwan IA, Saito S, Goto F.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11783812
4% tetracaine in 0.5% bupivacaine gave relief for 2 months ( some Hypesthesia =numbness for 2.2 weeks) – suspect would last a lot longer if just post herpetic rather than tirgeminal.
Int J Clin Pract. 2008 Feb;62(2):248-54. Epub 2007 Nov 23.
Efficacy and safety of high concentration lidocaine for trigeminal nerve block in patients with trigeminal neuralgia.
Han KR, Kim C, Chae YJ, Kim DW.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18036166
- 10% lidocaine in 7.5% glucose – 0.2 ml for Gasserian ganglion bloch (GGB) and 0.7 ml for rest
- Block types -infraorbital nerve block (IONB) 4 – all responded
superior orbital nerve block (SONB), 2 – all responded
maxillary nerve (V2) block, 5 – 4/5 responded
mandibular nerve (V3) block 11 – 6/11 responded
Gasserian ganglion block (GGB) 13 – 6/13 responded - 12 cases = 34.3% of 35 cases responded favorably lasting 3-172 weeks – the more peripheral blocks all responed – more central blocks responded about 1/2 the time
- 4 cases got some numbnesss to area that recovered within 6 months
Reg Anesth Pain Med. 1998 Jan-Feb;23(1):96-100.
The use of 5% lidocaine for prolonged analgesia in chronic pain patients: a new technique.
Choi YK, Liu J.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9552786
- 5 % lidocaine in 7.5% dextrose
- one case each of occipital and trigeminal block lasting 8-14 months
- one case intercostal lasting 5 weeks but of course repeatable
Adverse effect profile of Lidocaine injections for occipital nerve
block in occipital neuralgia
Soma Sahai-Srivastava, Dawood Subhani
J Headache Pain (2010) 11:519–523
- Preferred using 5% lidocaine but found elderly more likely to get dizzy from injections
- I found using 5%, unlikely to have problems if stick to 2 mls for usual adults, and under 1-1.5 for elderly.
- Cannot be injected close to spine as inadvertant spinal can be deadly
- Need to tell patient will be sore for a few days – the semineurolytic effects hurt.
In real life, when patient comes back in a week still growning in pain – they get another block a week later… – some could take 3 times to get a good block especially with 5 % lidocaine – but without fears of dysesthesia uncomfortable numb feeling pains – thtat you can get from alcohol or phenol.
Comment – pulse radiofrequency is not available here. I make up 60% lidocaine (autoclave but do not use vent at end – just unplug autoclave otherwise will boil over in vent) and dilute to 6% with sterile D5W. For serious injections, I use 5% lidocaine to dilute pontocaine injectable powder to 5% – or use 10% lidocaine. For occipital neuralgia, I give a botox shot first (100 units into nerves and 100 units intradernal in sore areas.) – then the lidocaine shots a week or 2 later (maybe take 2 X a week apart).

Pingback: New Rx For Chronic Abdominal Pain – Pulse Radiofrequency to Bilateral T10-T11 | Pain Medical Musing