In a Quebec analysis (if one looks is actually the drug company’s), it has been suggested that Duloxetine might be more cost effective for patients over 65 where the heart disease and stomach bleed risks of NSAID arthrtis pill might be too great. However Clinically significant help of Duloxetine has been questioned.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012 Dec 17. [Epub ahead of print]
The Cost-Effectiveness of Duloxetine in Chronic Low Back Pain: a Quebec Societal Perspective.
Wielage R, Bansal M, Wilson K, Klein R, Happich M. Affiliations: 1Medical Decision Modeling Inc. 2Eli Lilly Canada 3Lilly Deutschland GmbH.
Unfortunately this article appears generated by the drug company. The article states that Duloxetine is effective in low back pain:
“Duloxetine is a selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor which has demonstrated analgesic effects in two CLBP randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and an effect approaching statistical significance in a third 17–19.
They reference 3 studies on use of duloxetine in back pain – all produced by the company involved.
17. Skljarevski V, Ossanna M, Liu-Seifert H, et al. A double-blind, randomized trial of duloxetine versus placebo in the management of chronic low back pain. Eur J Neurol
2009;16:1041–8.
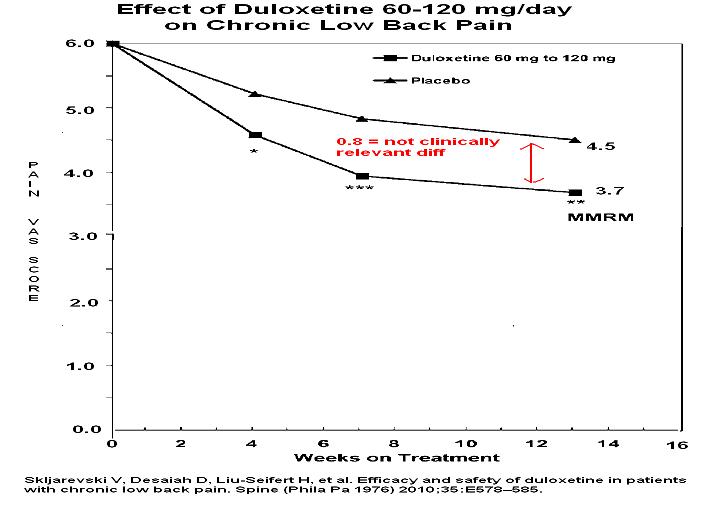
18. Skljarevski V, Desaiah D, Liu-Seifert H, et al. Efficacy and safety of duloxetine in patients with chronic low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35:E578–585.
19. Skljarevski V, Zhang S, Desaiah D, et al. Duloxetine versus placebo in patients with chronic low back pain: a 12-week, fixed-dose, randomized, double-blind trial. J Pain
2010;11:1282–90.
What actually happened is that it was only found effective in 2/3 trials. One of the trials was published in prestigious medical journal SPINE:
Skljarevski V, Desaiah D, Liu-Seifert H, et al.
Efficacy and safety of duloxetine in patients with chronic low back pain.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35:E578–585.
There was an editorial that cast doubt on the significance of results:
Point of View
Efficacy and Safety of Duloxetine in Patients With Chronic Low
Back Pain
Richard A. Deyo, MD, MPH
SPINE 2010;35:E586
Concerns were:
- Only company- allowed incomplete data was available so could be biased and “selective reporting” possible
- High (27%) drop out rate meant that those who were doing pororly dropped out – artifically increasing the study’s overall effectiveness
- analysis done behind closed doors might lead to “some errors and some poor practices”
- Company based studies tend to get better results than non-company based studies as a whole
- Results obtained might be statistically better but are not clinically relevant improvement levels
Even the food and drug association (FDA) wants a clinical difference of at least one for minimal effectiveness
mentioned in: FDA Approves Tapentadol ER for Diabetic Neuropathy. Pauline Anderson. Medscape Aug 29, 2012 free if register here
Addendum – you probably have not heard much from manufacturer on abilities of cymbalta. This is perhaps because a lesson was learnt by manufacturers of original lyrica and gabapentin. Both had to pay big fines for overstating their product. FDA requires a drop of VAS of >1 to be clinically relevant. 0.9 doesn’t do that for back pain overall. What about knee pains?
This was summarized in:
Ther Adv Musculoskel Dis(2013) 5(6) 291–304
Clinical experience with duloxetine in the management of chronic musculoskeletal pain. A focus on osteoarthritis of the knee
Jacques P. Brown and Luc J. Boulay
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3836379/pdf/10.1177_1759720X13508508.pdf
Chappell, A., Ossanna, M., Liu-Seifert, H., Iyengar, S., Skljarevski, V., Li, L. et al. (2009c) Duloxetine, a centrally acting analgesic, in the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis knee pain: a 13-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Pain 146: 253–260
a 0.84 difference from placebo
Chappell, A., Desaiah, D., Liu-Seifert, H., Zhang, S., Skljarevski, V., Belenkov, Y. et al. (2011) A double blind,randomized, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of duloxetine for the treatment of chronic pain due to osteoarthritis of the knee. Pain
Pract 11: 33–41.
0.84 again
Frakes, E., Risser, R., Ball, T., Hochberg, M. and Wohlreich, M. (2011) Duloxetine added to oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for treatment of knee pain due to osteoarthritis: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Curr Med Res Opin 27: 2361–2372
a 0.91
So duloxetine at least in these studies (using postherpetic neuralgia cases is cheating because most will respond well to anything) could NOT achieve the golden goose of decreasing pain Visual Analog Scale by over 1/10 over placebo. How do they get mention? Because they spend great efforts going over subgroup analysis – giving you results of “responders”.
– hey – someone set me straight!